Selecting items, and View settings
You can select an atom, bond, or residue by right-clicking on it. Only one of these selection categories can be used at a time. To change which, use the View/Sel level dropdown in the view section of the UI. Hotkeys for cyling: ; and '. You can deselect an item by right clicking it again, selecting another item, or pressing the Esc key. You can cycle through items using the next atom (or next bond etc, depending on the view/selection level), or their hotkeys, Left arrow and Right arrow.

Selected items are rendered in red.
In addition to affecting selection behavior, View/Sel level also changes the color scheme of the displayed molecule. In Residue mode, it colors each residue together instead of color coding by atom.
Information display
The UI displays a consise bit of data for the selected item; its contents depend on the type of selection. See the examples below:
Atom selection data:

Bond selection data displays two lengths: Both the instantaneous, measured length, and the
equilibrium length maintained by force field bonded parameter. It also includes the oscillation
frequency around this length, derived from the force field.

Residue selection data:

When you select an atom or bond in a small organic molecule, that molecule is set as the active molecule.
Currently, Daedalus only supports selecting a single item at a time.
Color codes
By default, atoms are color-coded using the typical CPK scheme. We have mimicked the specific colors used by PyMol in some cases. For example, Carbon atoms are green, oxygen atoms are red, nitrogen blue, hydrogen white. Alternate color schemes are available depending on the Vew / Sel level: If atom or bond is set, you can color atoms by partial charge. If Residue is set, you can color by the residue's position, e.g. in its polypeptide chain. In both cases, we use the Viridis color map to smoothly display the transition between positive and negative charge, or first and last residue.
To enable these, select the Color by q or Color by res UI items.
Example of a small molecule colored in CPK:
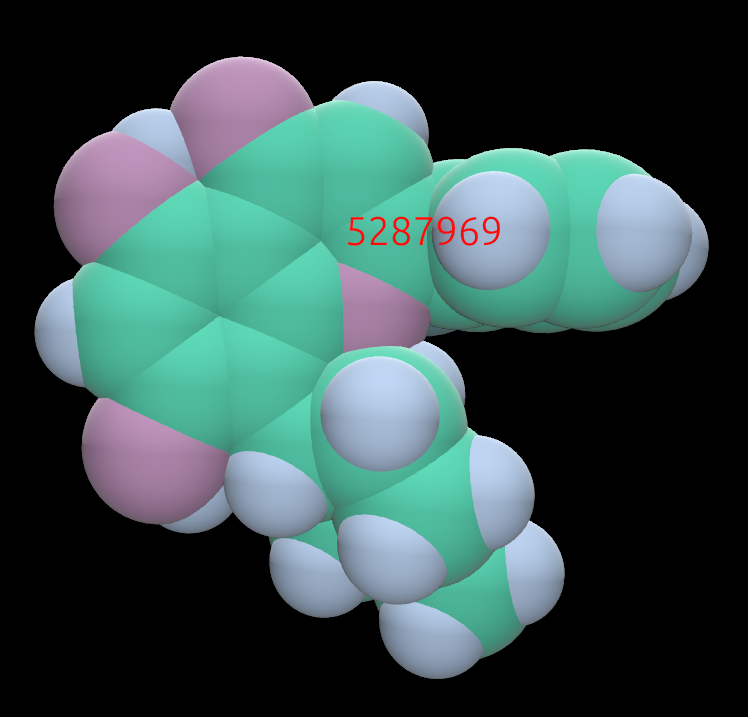
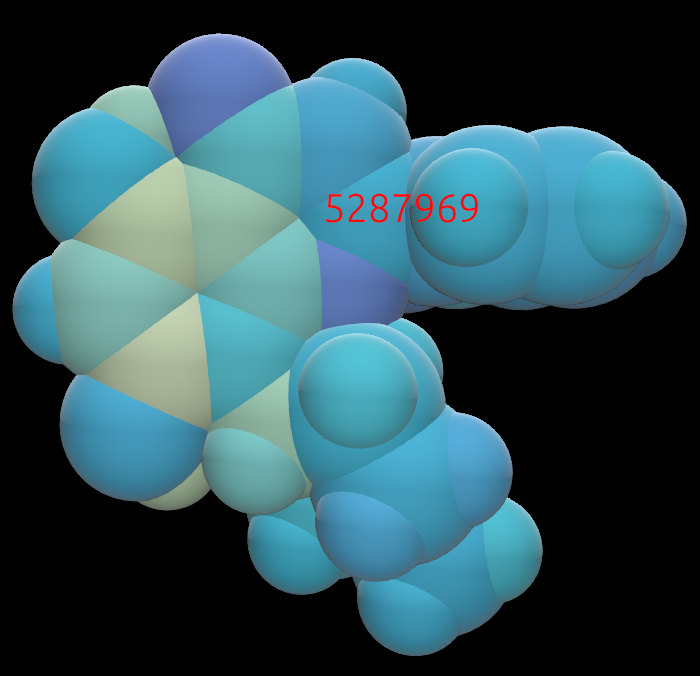
The same molecule, colored by partial charge. Yellow is positive charge; purple is negative.:
Example of residues colored by position in sequence:
